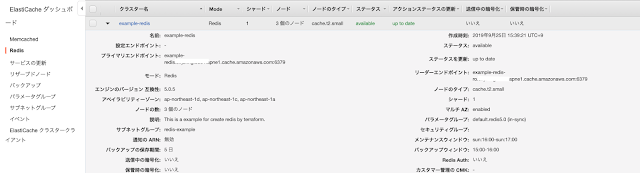
$ terraform apply
An execution plan has been generated and is shown below.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# aws_instance.example will be created
+ resource "aws_instance" "example" {
+ ami = "ami-031b61f0c1afb3454"
+ arn = (known after apply)
+ associate_public_ip_address = (known after apply)
+ availability_zone = (known after apply)
+ cpu_core_count = (known after apply)
+ cpu_threads_per_core = (known after apply)
+ get_password_data = false
+ host_id = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ instance_state = (known after apply)
+ instance_type = "t3.nano"
+ ipv6_address_count = (known after apply)
+ ipv6_addresses = (known after apply)
+ key_name = (known after apply)
+ network_interface_id = (known after apply)
+ password_data = (known after apply)
+ placement_group = (known after apply)
+ primary_network_interface_id = (known after apply)
+ private_dns = (known after apply)
+ private_ip = (known after apply)
+ public_dns = (known after apply)
+ public_ip = (known after apply)
+ security_groups = (known after apply)
+ source_dest_check = true
+ subnet_id = (known after apply)
+ tenancy = (known after apply)
+ volume_tags = (known after apply)
+ vpc_security_group_ids = (known after apply)
+ ebs_block_device {
+ delete_on_termination = (known after apply)
+ device_name = (known after apply)
+ encrypted = (known after apply)
+ iops = (known after apply)
+ kms_key_id = (known after apply)
+ snapshot_id = (known after apply)
+ volume_id = (known after apply)
+ volume_size = (known after apply)
+ volume_type = (known after apply)
}
+ ephemeral_block_device {
+ device_name = (known after apply)
+ no_device = (known after apply)
+ virtual_name = (known after apply)
}
+ network_interface {
+ delete_on_termination = (known after apply)
+ device_index = (known after apply)
+ network_interface_id = (known after apply)
}
+ root_block_device {
+ delete_on_termination = (known after apply)
+ encrypted = (known after apply)
+ iops = (known after apply)
+ kms_key_id = (known after apply)
+ volume_id = (known after apply)
+ volume_size = (known after apply)
+ volume_type = (known after apply)
}
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
aws_instance.example: Creating...
aws_instance.example: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
aws_instance.example: Creation complete after 16s [id=i-054c4a5d5f65d7633]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
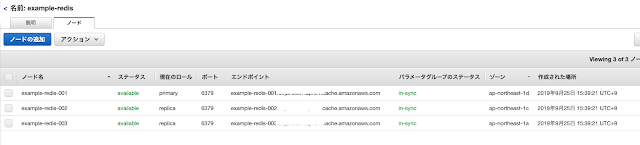
terraform show コマンドを使ってインスタンを確認します。
$ terraform show
# aws_instance.example:
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-031b61f0c1afb3454"
arn = "arn:aws:ec2:ap-northeast-1:994787028884:instance/i-054c4a5d5f65d7633"
associate_public_ip_address = true
availability_zone = "ap-northeast-1a"
cpu_core_count = 1
cpu_threads_per_core = 2
disable_api_termination = false
ebs_optimized = false
get_password_data = false
id = "i-054c4a5d5f65d7633"
instance_state = "running"
instance_type = "t3.nano"
ipv6_address_count = 0
ipv6_addresses = []
monitoring = false
primary_network_interface_id = "eni-068a1099ebe134ed4"
private_dns = "ip-172-31-45-252.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal"
private_ip = "172.31.45.252"
public_dns = "ec2-13-231-108-188.ap-northeast-1.compute.amazonaws.com"
public_ip = "13.231.108.188"
security_groups = [
"default",
]
source_dest_check = true
subnet_id = "subnet-8a04efc2"
tenancy = "default"
volume_tags = {}
vpc_security_group_ids = [
"sg-3b359644",
]
credit_specification {
cpu_credits = "unlimited"
}
root_block_device {
delete_on_termination = true
encrypted = false
iops = 300
volume_id = "vol-03eedb71c41a89002"
volume_size = 100
volume_type = "gp2"
}
}